Course Glossary
Here are some words that you should be familiar with for this course.
Unless otherwise noted, definitions from Wiktionary. CC BY SA
Special | A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | ALL
S |
|---|
SettingNoun
setting (plural settings)
| |
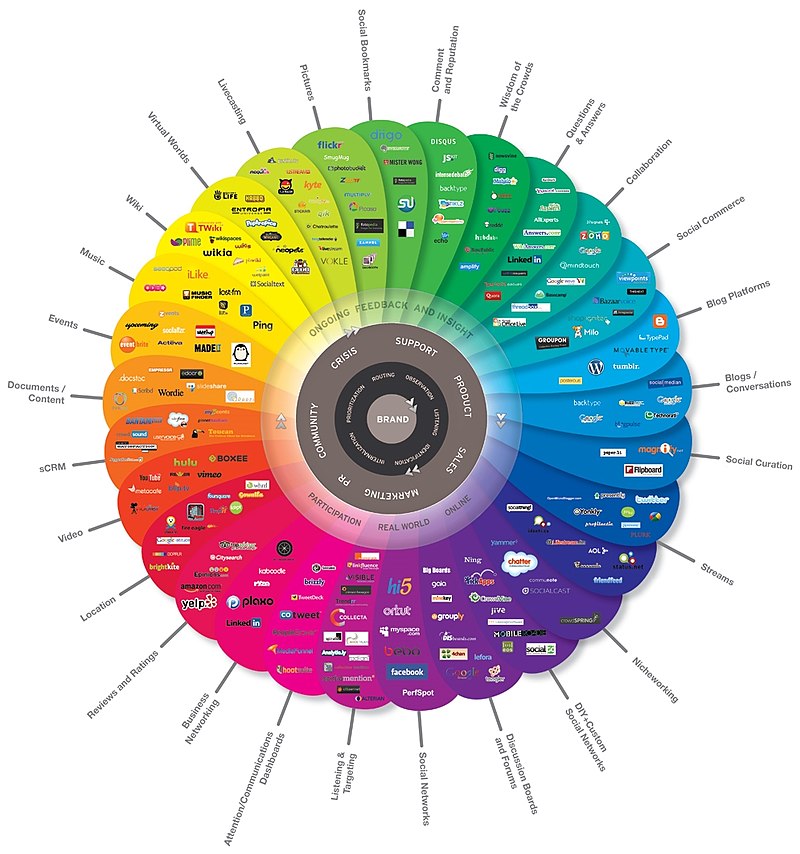
Social Networks
Computer-mediated tools that allow people to create, share or exchange information, ideas, and pictures/videos in virtual communities and networks. | |
StructureManner in which a building or other complete whole [like an academic paper] is constructed, supporting framework or whole of the essential parts of something (the structure of a poem, sentence, etc.) (Oxford Concise Dictionary). A Guide to Reading and Analyzing Academic Articles, by Amanda Graham, 1997-2012, is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs 3.0 Unported License. | |
StyleRefers to the way a writer expresses his or her ideas. Oxford Concise Dictionary: “manner of writing, speaking, or doing, in contrast to the matter to be expressed or thing done; collective characteristics of the writing or diction or way of presenting things.” A Guide to Reading and Analyzing Academic Articles, by Amanda Graham, 1997-2012, is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs 3.0 Unported License. | |
SummaryAdjective
summary (comparative more summary, superlative most summary)
| |
 For the context of this course we will be using the terms Social Networks and Social Media interchangeably.
For the context of this course we will be using the terms Social Networks and Social Media interchangeably.