| acute angle | An angle measuring less than 90º. |
| acute triangle | A triangle with three angles that each measure between 0º and 90º. |
| angle | A figure formed by the joining of two rays with a common endpoint. |
| area | The amount of space inside a two-dimensional shape, measured in square units. |
| circumference | The distance around a circle, calculated by the formula C = 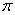 d. d. |
| complementary angles | Two angles whose measurements add up to 90º. |
| cone | A solid figure with a single circular base and a round, smooth face that diminishes to a single point. |
| congruent | Having the same size and shape. |
| corresponding angles | Angles of separate figures that are in the same position within each figure. |
| corresponding sides | Sides of separate figures that are opposite corresponding angles. |
| cube | A six-sided polyhedron that has congruent squares as faces. |
| cylinder | A solid figure with a pair of circular, parallel bases and a round, smooth face between them. |
| diameter | The length across a circle, passing through the center of the circle. A diameter is equal to the length of two radii. |
| equilateral triangle | A triangle with 3 equal sides. Equilateral triangles also have three angles that measure the same. |
| face | The flat surface of a solid figure. |
| hypotenuse | The side opposite the right angle in any right triangle. The hypotenuse is the longest side of any right triangle. |
| isosceles trapezoid | A trapezoid with one pair of parallel sides and another pair of opposite sides that are congruent. |
| isosceles triangle | A triangle with 2 equal sides and 2 equal angles. |
| leg | In a right triangle, one of the two sides creating a right angle. |
| line | A line is a one-dimensional figure, which extends without end in two directions. |
| line segment | A finite section of a line between any two points that lie on the line. |
| obtuse angle | An angle measuring more than 90º and less than 180º. |
| obtuse triangle | A triangle with one angle that measures between 90º and 180º. |
| parallel lines | Two or more lines that lie in the same plane but which never intersect. |
| parallelogram | A quadrilateral with two pairs of parallel sides. |
| perimeter | The distance around a two-dimensional shape. |
| perpendicular lines | Two lines that lie in the same plane and intersect at a 90º angle. |
| pi | The ratio of a circle’s circumference to its diameter. Pi is denoted by the Greek letter 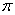 . It is often approximated as 3.14 or . It is often approximated as 3.14 or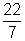 . . |
| plane | In geometry, a two-dimensional surface that continues infinitely. Any three individual points that don't lie on the same line will lie on exactly one plane. |
| point | A zero-dimensional object that defines a specific location on a plane. It is represented by a small dot. |
| polygon | A closed plane figure with three or more straight sides. |
| polyhedron | A solid whose faces are polygons. |
| pyramid | A polyhedron with a polygonal base and a collection of triangular faces that meet at a point. |
| Pythagoras | A Greek philosopher and mathematician who lived in the 6th Century B.C. |
| Pythagorean Theorem | The formula that relates the lengths of the sides of any right triangle: 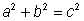 , where c is the hypotenuse, and a and b are the legs of the right triangle. , where c is the hypotenuse, and a and b are the legs of the right triangle. |
| quadrilateral | A four-sided polygon. |
| radius | The distance from the center of a circle to any point on the circle. |
| ray | A half-line that begins at one point and goes on forever in one direction. |
| rectangle | A quadrilateral with two pairs of parallel sides and four right angles. |
| rectangular prism | A polyhedron that has three pairs of congruent, rectangular, parallel faces. |
| rhombus | A quadrilateral with four congruent sides. |
| right angle | An angle measuring exactly 90º. |
| right triangle | A triangle containing a right angle. |
| scalene triangle | A triangle in which all three sides are a different length. |
| similar | Having the same shape but not necessarily the same size. |
| sphere | A solid, round figure where every point on the surface is the same distance from the center. |
| square | A quadrilateral whose sides are all congruent and which has four right angles. |
| straight angle | An angle measuring exactly 180º. |
| supplementary angles | Two angles whose measurements add up to 180º. |
| trapezoid | A quadrilateral with one pair of parallel sides. |
| triangle | A polygon with three sides. |
| vertex | A turning point in a graph. Also the endpoint of the two rays that form an angle. |
| volume | A measurement of how much it takes to fill up a three-dimensional figure. Volume is measured in cubic units. |
![]() d.
d.![]() . It is often approximated as 3.14 or
. It is often approximated as 3.14 or![]() .
.![]() , where c is the hypotenuse, and a and b are the legs of the right triangle.
, where c is the hypotenuse, and a and b are the legs of the right triangle.